Relentlessly Improving the Performance of our GPU Query Engine, Theseus
By Voltron Data
Voltron Data

Author(s):

Published: September 10, 2024
3 min read
Theseus is Built for Accelerated Systems
NVIDIA does not sell GPUs, they sell accelerated systems, combining processors, networking, storage, and software to win every benchmark.
It’s for this reason Theseus, our distributed query execution engine, is accelerator-native. To take full advantage of NVIDIA hardware, we also integrate a lot of NVIDIA software (e.g., RAPIDS libcudf, NVComp, GPUDirect Storage, and more) gaining outsized performance gains and a long list of opportunities to get better.
Performance Over Time
We announced Theseus to the world almost a year ago at HPE’s Discover in Barcelona, and at NVIDIA’s GTC 2024 in March this year we showed our first public benchmarks and our views on honest benchmarking. Leading up to GTC, and continuing ever since Theseus’ performance has been rapidly improving.
At Voltron Data we take benchmarking seriously. Our pre-merge benchmarks include a full suite of TPC-H SF10K (10TB), and nightly we benchmark TPC-H SF100K (100TB) along many other benchmarks to ensure the engine only gets faster and cheaper.
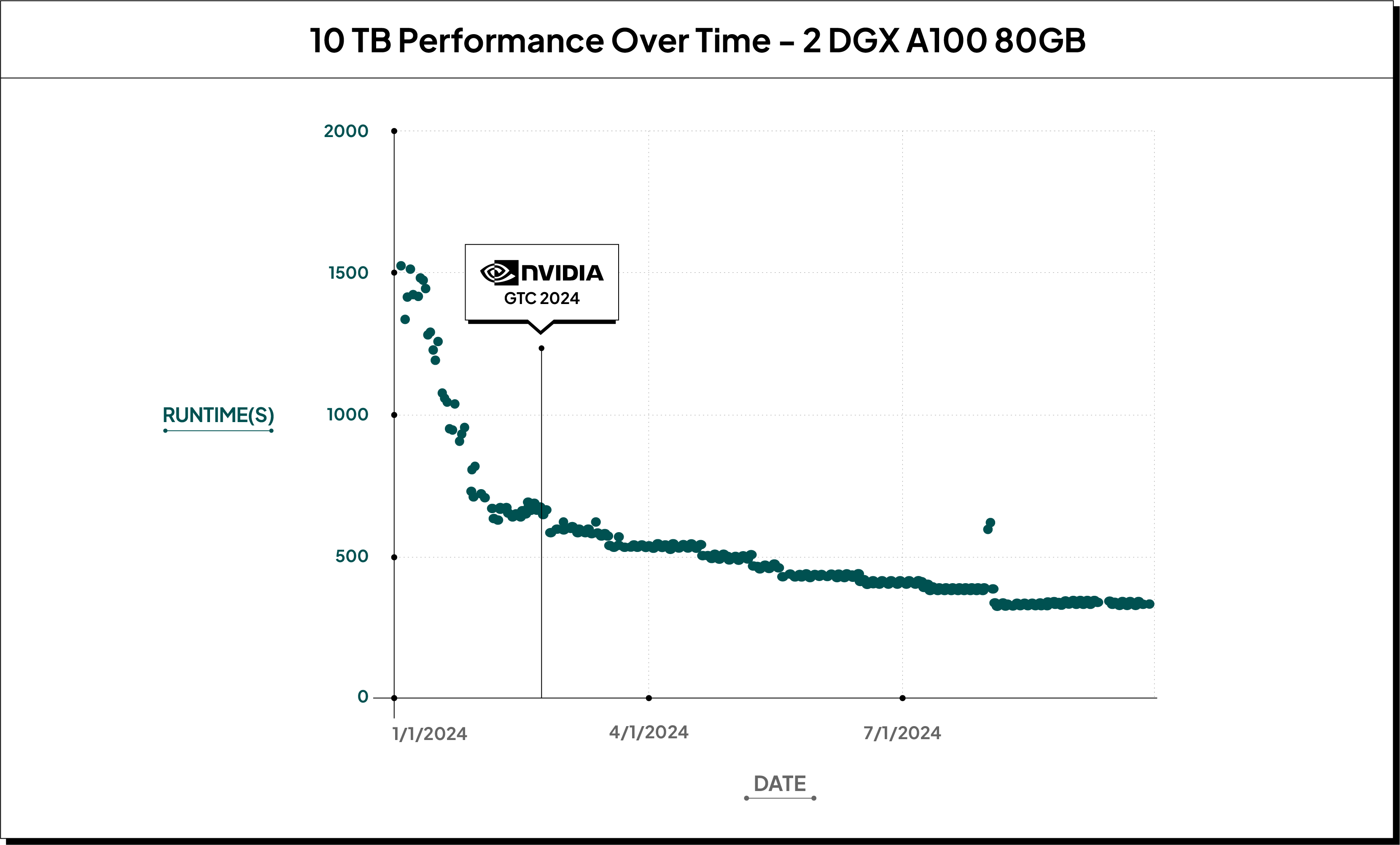
Ten Terabytes (SF10K)
If we look at the total benchmark runtimes for TPC-H SF10K (10TB) on 2 servers (DGX A100 640GB) you can see that since GTC 2024 performance has almost doubled, going from 9.5 minutes to under 5.5 minutes, bringing the cost of the benchmark run from $3.54 to $2.19.
One Hundred Terabytes (SF100K)
We’re even more excited about the changes we’ve seen in TPC-H SF100K (100TB). When looking at 10 servers (DGX A100 640GB). Not only did we almost double our performance, but we were able to improve memory usage to scale down the number of servers needed to do a full 100TB run.
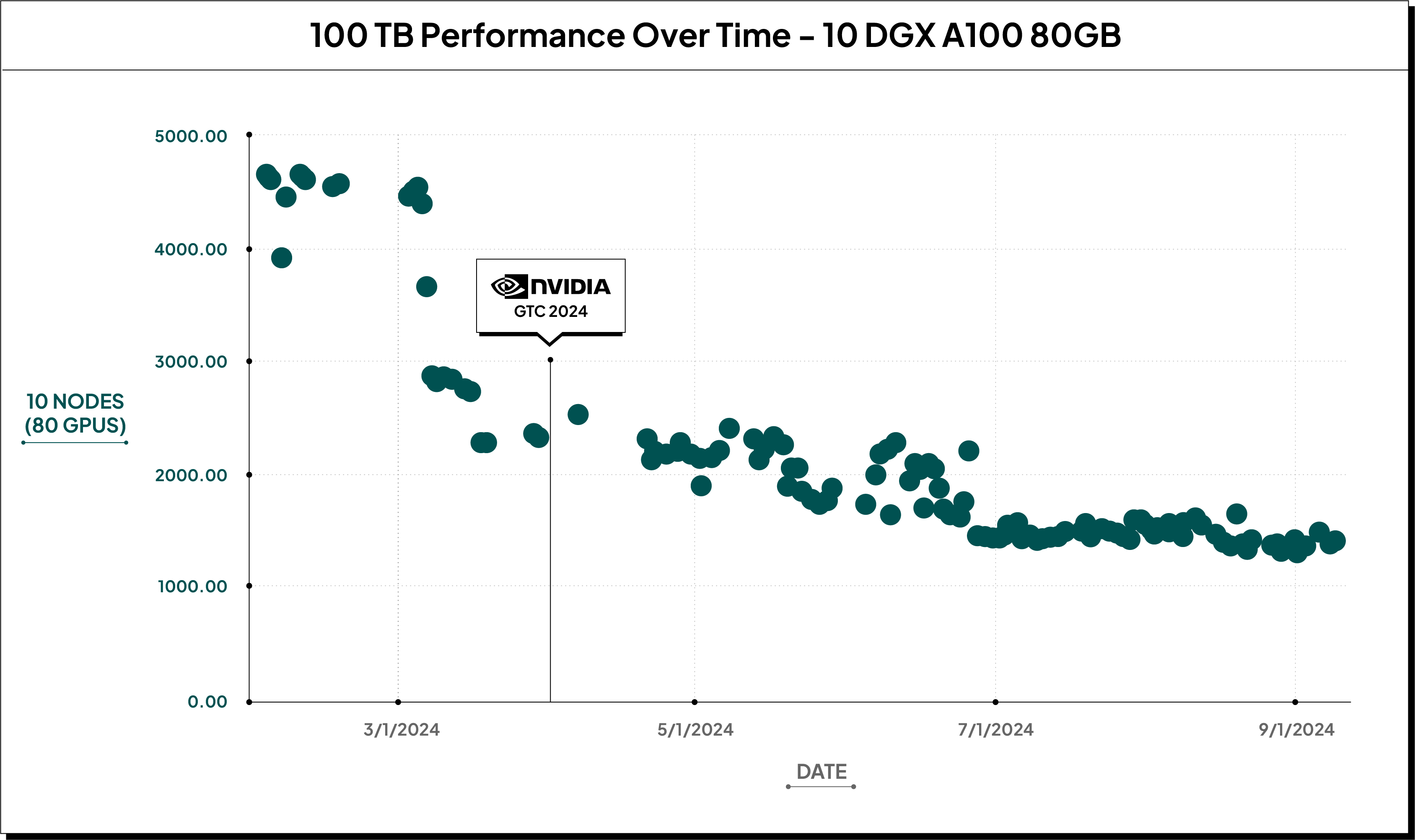
These performance gains brought the cost of a 100TB run down from $86 to $43.44 at 10 nodes.
What’s Next
We still have a long way to go with accelerator-native performance, and you can expect to see more posts like this in the coming months where we continue to push the state-of-the-art.
We’ve been doing this for a long time, and our CEO said it perfectly in the original Relentlessly Improving Performance post 4 years ago.
“By considering both software and hardware holistically, the RAPIDS team is making the vast potential of accelerated computing accessible to data practitioners across industries and institutions.”
-Josh Patterson, Co-Founder and CEO of Voltron Data
We couldn’t agree more. To see the latest Theseus benchmarks, please visit: voltrondata.com/benchmarks/theseus
Previous Article
Keep up with us



